Taiwan Tower
a 380m tower with observation decks, destined to serve as a tourist attraction, and symbolize modern Taiwan
Taichung Gateway Park, Taichung, Taiwan
2011
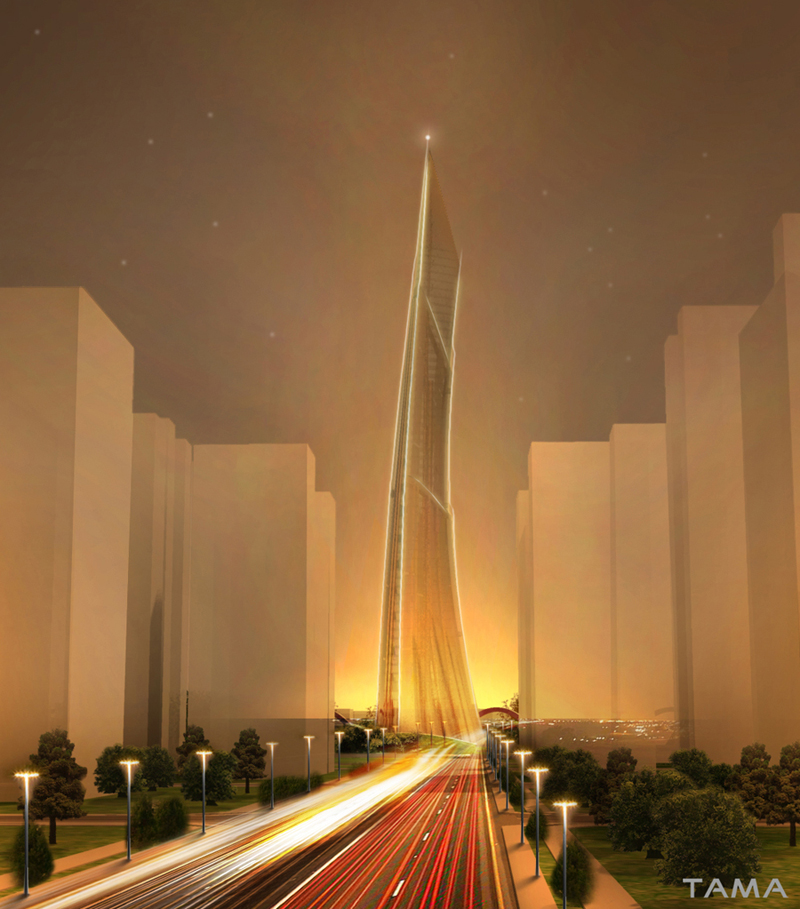
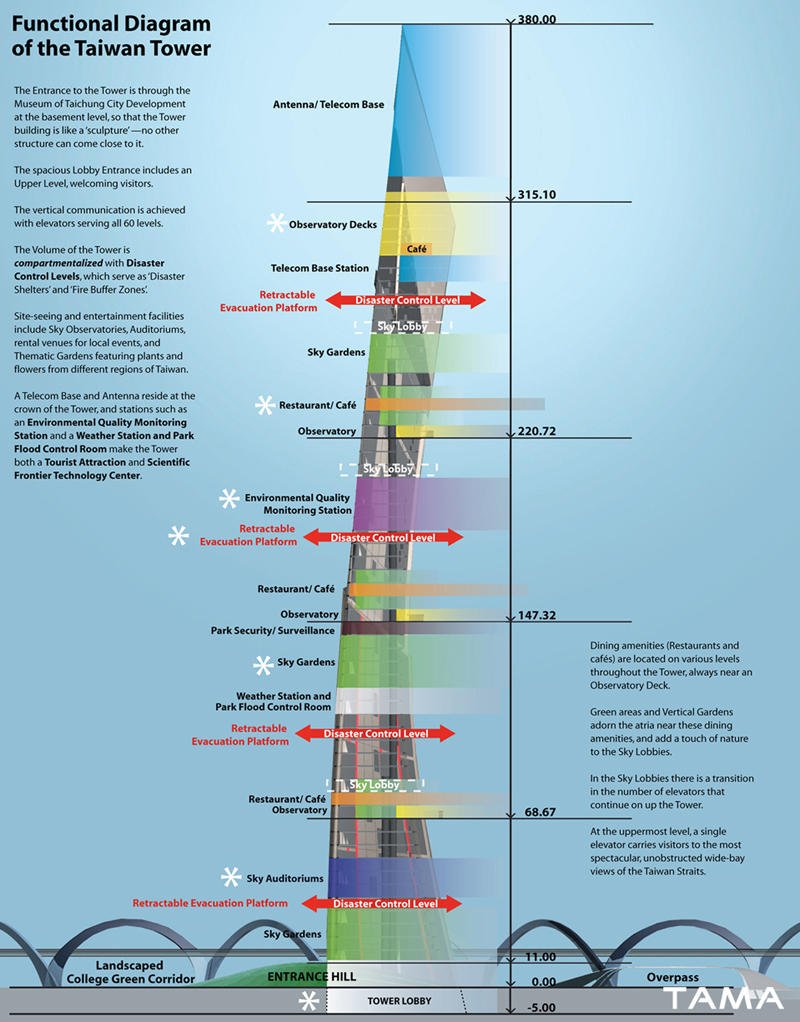
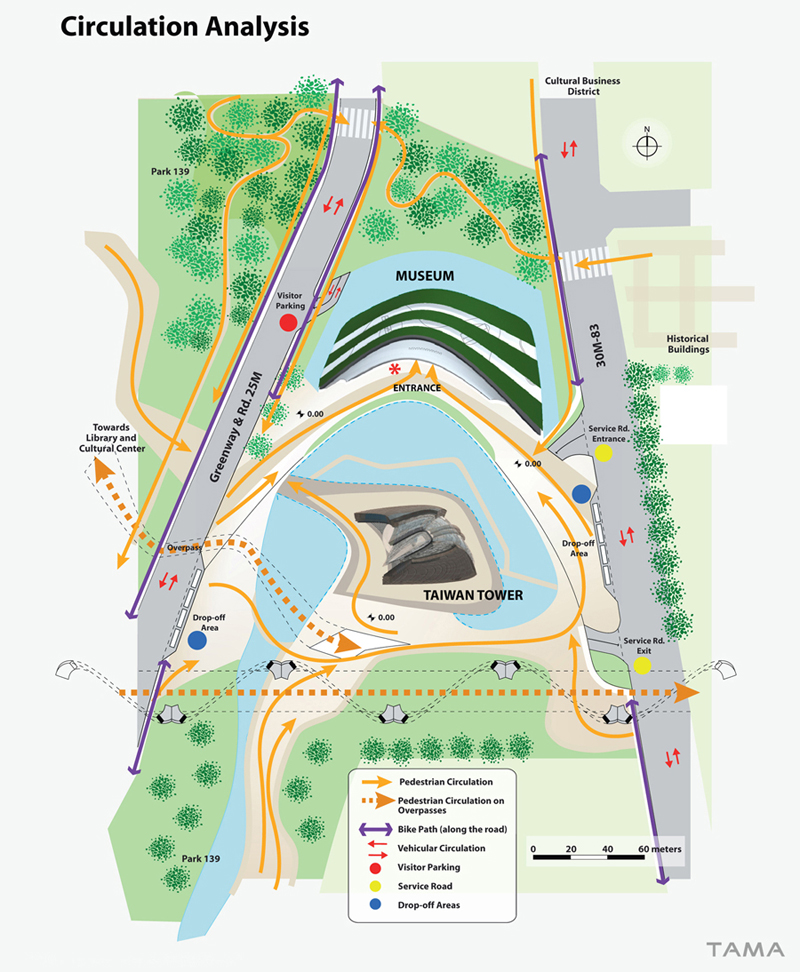
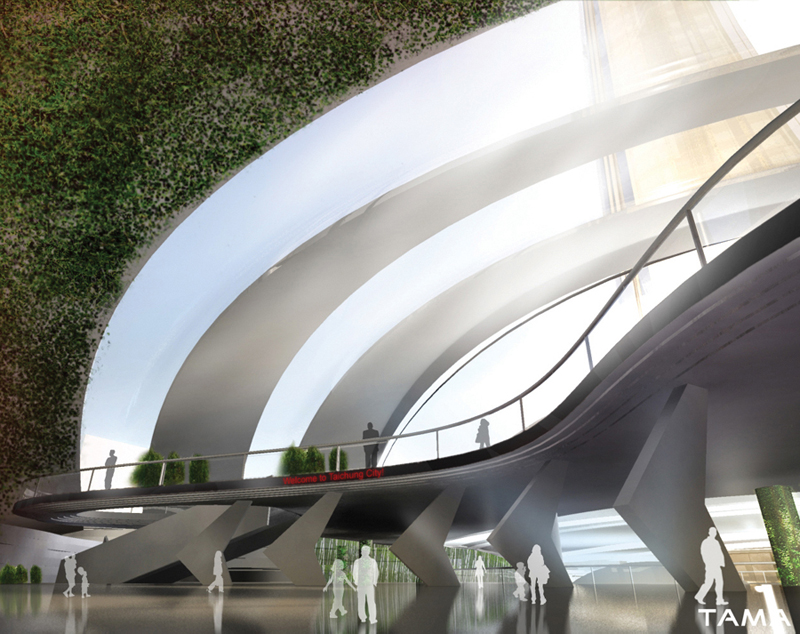
The Taiwan Tower was considered a stand-alone sculpted piece of art, a 380m stylized obelisk cambered in a way to be facing in the direction of the Taiwan Straits over Dadu Mountain, emerging taut and proud, symbolizing the optimism with which the people of Taiwan look at the future. Nothing seemed capable to touch it at the base to form an entrance –there is no attached volume, just a reflective pond to keep visitors at a respectful distance from the structure whose height they can see in its reflection without having to bend over backwards to turn their gaze skyward. Access to the Tower is placed through a juxtaposed hill-shaped entrance, bringing the visitor to the Tower Lobby located under the pond. The Tower Lobby is a spacious, sunlit environment, linking directly to the Museum of Taichung City Development and other amenities of the Tower. The Taiwan Tower has a small, discreet shadow footprint, varying in shape during the day.
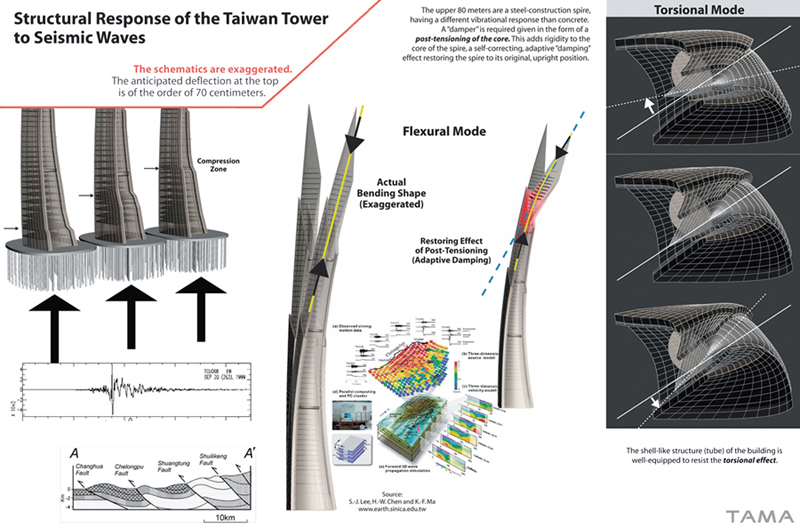
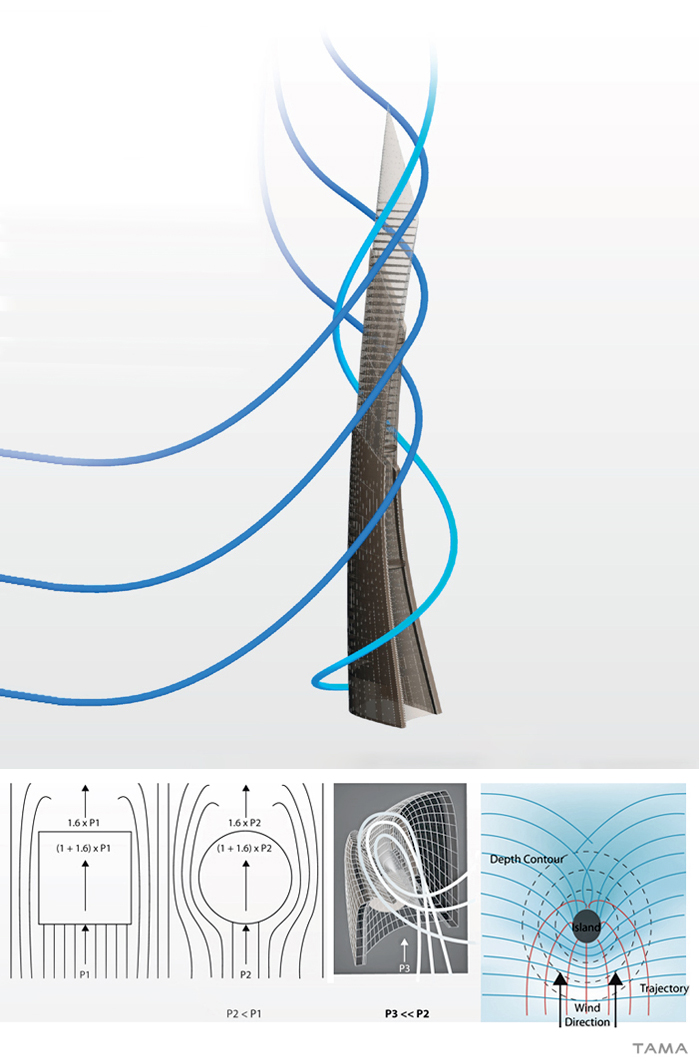
Among the key elements on which Tower is designed, is the fact that it is located on the Class 1 active Chelungpu fault, which, on September 21, 1999, caused a 7.3 Richter earthquake, that caused more than 2,300 deaths. The spectral characteristics of the long-period seismic waves that were recorded near the fault requires the structure to use a deep pile foundation on a slab, to improve the bearing capacity of the earth underneath the Tower, providing a damping effect to the oncoming seismic waves, and thus reducing the possibility of liquefaction. Wind forces are affected ultimately by the Planetary Boundary Layer structure of the wind profile. Asymmetric devices are created on the shell of the Taiwan Tower to induce wind to flow behind the structure to take advantage of the Corriolis Force, reducing the wind pressure and drag dramatically.
Unlike traditional towers which are based on a frame-type structure requiring additional material to overcome large displacements, the building envelop is used as a primary, load-bearing, structural element, behaving like a shell, reducing the overall use of structural material. Eco-friendly building materials along with interior green planting with vertical green walls enhance the overall architecture, creating a living interior design. The surface of the Tower, covered with self-cleaning glass, will collect runoff into reservoirs for use after filtering and conditioning. Remaining runoff will be channelized to the overall stormwater detention and management system, improving the sustainability and economy of the overall Park master plan, also offering the added protection of controlling groundwater levels.
The design is unique to Taichung city, with signature traits immediately recognizable. In the same way that the Eiffel Tower spells Paris, the Taiwan Tower must immediately bring to mind the city of Taichung and Taiwan.